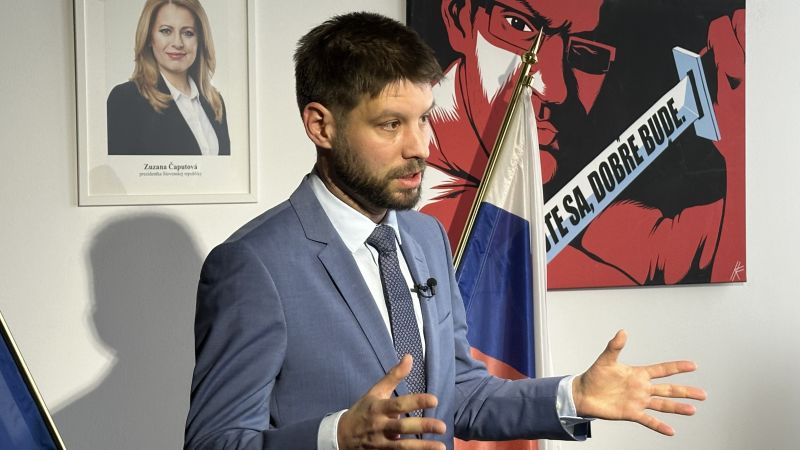
A fake recording of a candidate saying he’d rigged the election went viral. Experts say it’s only the beginning::Days before a pivotal election in Slovakia to determine who would lead the country, a damning audio recording spread online in which one of the top candidates seemingly boasted about how he’d rigged the election.
I voted for him and I didnt know about this ai audio. Primary social media in Slovakia is FB and I stopped using that like 8 years ago, that’s probably why.
FB is cancer, and I’m not sure how it will ever actually disappear.
Fundamentally we as a species have lost the use of face and voice in a video to establish authenticity.
A person can spoof an email, and we have cryptographic signatures as a means of authentication.
So if I record myself saying something I could sign the video I guess (implementation TBD lol).
But what if someone else (news agency say) takes a video of someone else, how do we authenticate that?
If it’s a news agency they could sign it. Great.
But then we have the problem of incentives, too. Does the benefit of a fake outweigh the detrimental effects for said news agency?
The most damage would be to the person being videoed (reputation, loss of election, whatever). There would be less damage to the media company (“oops so sorry please stay subscribed”). You could add fines but corporate oversight is weak. And the benefit of releasing a fake would be clicks and money so a news company would be a lot more likely to pass along a fake as real.
So I guess I have no idea what we do. At the moment we are fucked. Yay.
If it’s a news agency they could sign it. Great.
But then it hinders the denouncing of police violence, whistleblowing, and allows corporations to sign their claims while what regular people record will be assumed to be false
Edit: reporting can also be done as a second hand account, reposting videos/photos already in circulation, meaning that either a news company will sign those second hand recordings at the risk of validating AI content, or only their own corporate recordings will be used.
No one wins in any case
Vocal chord implants which sign whatever you’re saying and emit the signature with ultrasound.
When I was growing up I was told to never trust anything I saw on the Internet.
You think people would do that? Just go on the internet and tell lies?
And why should I believe this?
The recordings immediately went viral on social media, and the candidate, who is pro-NATO and aligned with Western interests, was defeated in September by an opponent who supported closer ties to Moscow and Russian President Vladimir Putin.
Why is it always the Russian hackers? /s
Because they have state actors running around following the exact same foreign policy strategy as all the other international powers. Make sure your guy is in charge, and who cares how.
I’m sure commercial generative AI companies would be required to embed invisible/inaudible watermark in the generated contents soon, similar with how spotify and apple music watermarking songs in their streaming platform.
Doesn’t look like Spotify or Apple watermark music, although that author used them as a hypothetical example.
Universal Music Group used to but moved away from the practice, it seems.
Dangerous approach.
Bad actors will not watermark their output, or remove the watermark. All watermarking does is lend credibility to misinformation. It’s literally worse than nothing.
It won’t stop bad actors, but it’ll allow AI companies to cover their asses to avoid being blamed for misuse of their tech, which is one of the reason I think most AI companies will use it soon.
I’m sure you’re right on that. I think it’s already done.
Anybody could copypaste the article here? Would love to read it but apparently the site has issues with me using Firefox…
Days before a pivotal election in Slovakia to determine who would lead the country, a damning audio recording spread online in which one of the top candidates seemingly boasted about how he’d rigged the election.
And if that wasn’t bad enough, his voice could be heard on another recording talking about raising the cost of beer.
The recordings immediately went viral on social media, and the candidate, who is pro-NATO and aligned with Western interests, was defeated in September by an opponent who supported closer ties to Moscow and Russian President Vladimir Putin.
While the number of votes swayed by the leaked audio remains uncertain, two things are now abundantly clear: The recordings were fake, created using artificial intelligence; and US officials see the episode in Europe as a frightening harbinger of the sort of interference the United States will likely experience during the 2024 presidential election.
“As a nation, we are woefully underprepared,” said V.S. Subrahmanian, a Northwestern University professor who focuses on the intersection of AI and security.
Senior national security officials in the US have been gearing up for “deepfakes” to inject confusion among voters in a way not previously seen, a senior US official familiar with the issue told CNN. That preparation has involved contingency planning for a foreign government potentially using AI to interfere in the election.
State and federal authorities are also grappling with increased urgency to pass legislation and train election workers to respond to deepfakes, but limited resources within elections offices and inconsistent policies have led some experts to argue that the US is not equipped for the magnitude of the challenge, a CNN review found.
Already, the US has seen AI-generated disinformation in action.
In New Hampshire, a fake version of President Joe Biden’s voice was featured in robocalls that sought to discourage Democrats from participating in the primary. AI images that falsely depicted former President Donald Trump sitting with teenage girls on Jeffrey Epstein’s plane circulated on social media last month. A deepfake posted on Twitter last February portrayed a leading Democratic candidate for mayor of Chicago as indifferent toward police shootings.
Various forms of disinformation can shape public opinion, as evidenced by the widely held false belief that Trump won the 2020 election. But generative AI amplifies that threat by enabling anyone to cheaply create realistic-looking content that can rapidly spread online.
Political operatives and pranksters can pull off attacks just as easily as Russia, China or other nation state actors. Researchers in Slovakia have speculated that the vote-rigging deepfake their country faced was the work of the Russian government.
“I can imagine scenarios where nation state adversaries record deepfake audios that are disseminated using both social media as well as messaging services to drum up support for candidates they like and spread malicious rumors about candidates they don’t like,” said Subrahmanian, the Northwestern professor.
The FBI or Department of Homeland Security can move more swiftly to speak out publicly against a threat if they know that a foreign actor is behind a deepfake, said a senior US official familiar with the issue. But if an American citizen could be behind a deepfake, US national security officials would be more reluctant to counter it publicly out of fear of giving the impression that they are influencing the election or restricting speech, the official said.
And once a deepfake appears on social media, it can be nearly impossible to stop its spread.
“The concern is that there’s going to be a deepfake of a secretary of state who says something about the results, who says something about the polling, and you can’t tell the difference,” said the official, who was not authorized to speak to the press.
Efforts to regulate deepfakes and guard against their effects vary greatly among US states.
Some states including California, Michigan, Minnesota, Texas and Washington have passed laws that regulate deepfakes in elections. Minnesota’s law, for example, makes it a crime for someone to knowingly disseminate a deepfake intended to harm a candidate within 90 days of an election. Michigan’s laws require campaigns to disclose AI-manipulated media, among other mandates. More than two dozen other states have such legislation pending, according to a review by Public Citizen, a nonprofit consumer advocacy group.
CNN asked election officials in all 50 states about efforts to counter deepfakes. Out of 33 that responded, most described existing programs in their states to respond to general misinformation or cyber threats. Less than half of those states, however, referenced specific trainings, policies or programs crafted to respond to election-related deepfakes.
“Yes, this is something that keeps us all up at night,” said Alex Curtas, a spokesperson for New Mexico’s secretary of state, when asked about the issue. Curtas said New Mexico has plans for tabletop-exercises with local officials that will include discussion of deepfakes, but he said the state is still looking for tools to share with the public to help determine whether content has been generated with artificial intelligence.
Jared DeMarinis, Maryland’s administrator of elections, told CNN his state issued a rule that requires political ads that involve AI-generated content to include disclaimers, but he said he hopes the state legislature will pass a law that gives the state more authority on the issue.
“I don’t believe you can completely
Some efforts to combat disinformation have triggered more distrust. Last year, Washington’s secretary of state’s office signed a contract with a tech company to track election-related falsehoods on social media, which would include deepfakes, a spokesperson told CNN. But in November, the state’s Republican Party submitted an ethics complaint related to that contract, alleging the secretary was using public funds to pay a company to “surveil voters … suppressing opposition views.” The state ethics board declined to move forward on the complaint, which elicited more protest from the party.
Multiple pieces of federal legislation on election-related deepfakes have been proposed. US law currently prohibits campaigns from “fraudulently misrepresenting” other candidates, but whether that includes deepfakes is an open question. The Federal Election Commission has been considering the idea but has not reached a decision on the matter
How do we know it’s fake, and he’s not just claiming it’s fake? Unless I missed it the article doesn’t seem to cover that.
IMCO people claiming real recordings are AI fakes is going to be a bigger problem than actual fakes.
You might be kidding, but the answer is: The outcome plus Occam’s Razor.
a candidate saying he’d rigged the election
the candidate…was defeated
Which is more likely, that he was recorded while lying about rigging the election that he ended up losing or that the recording was faked?
He could just be really bad at rigging elections!
I guess I missed that rather obvious conclusion while I was looking for some technical explanation, thanks for pointing that out.
No worries.
I do agree with you that we’re likely to see just as many (if not more) guilty politicians claiming AI fakes when they’re caught red-handed as we will see framed politicians targeted with actual AI fakes. Just not in this case.
IMCO people claiming real recordings are AI fakes is going to be a bigger problem than actual fakes.
That’s a pretty bold claim considering we’ve already seen at least one fake impacting the US primary elections.
IMCO
I’m not familiar with this one. I assume “in my concerned opinion” but I really want it to be “in my cumble opinion”
Maybe “crappy?” I’m going to go with crappy.
Childish.
Cutesy
Calibrated